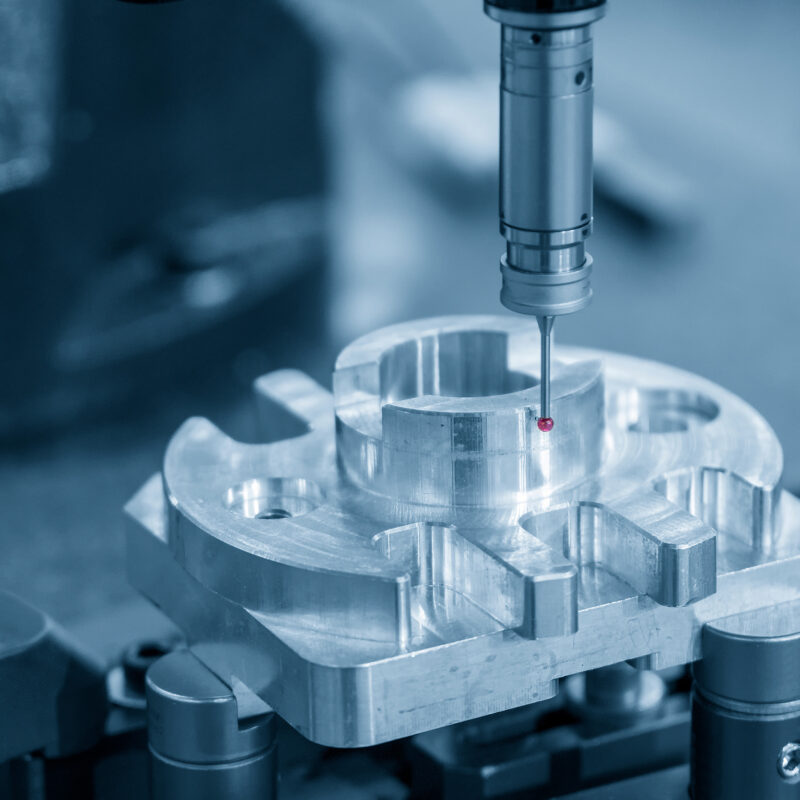
Metrology is the science of measurement that underpins all other science, and is integral in engineering and technical innovation, production quality and trade. Metrology’s impact is throughout modern societies, from laying the groundwork for technological advancements to boosting economic prosperity and promoting fair trade. Metrologists are people that practice metrology in the ongoing pursuit of higher accuracy and precision of measurements.
Good metrology provides consistency of product and process between organisations. Accurate and consistent measurement means we can trust that instruments are reporting correctly. An example of the importance of good metrology is the trust in measurements of components for precision engineered products from different suppliers- Think modern aircraft, consumer electronics or medical imaging equipment. The people practicing this science are metrologists.